In the digitally interconnected era, smart cards, as a crucial medium for identity recognition, data interaction, and scenario-based services, are permeating every corner of social life with greater intelligence and security. Wenlin Technology has been deeply engaged in the smart card field for years, establishing a comprehensive chip product matrix covering IC (high frequency), ID (low frequency), and UHF (ultra-high frequency). This matrix is tailored to various card manufacturing scenarios, meeting your diverse and personalized card production needs while providing solid and reliable hardware support for the card manufacturing industry.
The following Wenlin Technology will introduce the commonly used IC (high frequency), ID (low frequency) and UHF (ultra high frequency) smart card chips.
1.IC (high frequency) Frequency 13.56Mhz
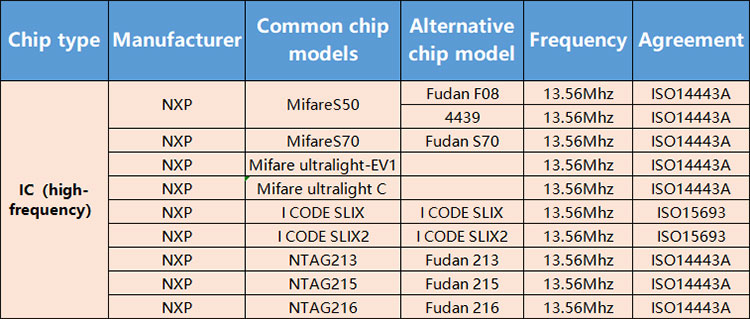
IC (high frequency) feature:The high-frequency chip also adopts inductive coupling, with a communication distance of 0-10 centimeters. It supports multi-tag reading (with a mature anti-collision mechanism), has a large storage capacity (128-bit to 8KB), and features high security (such as encryption coprocessors). Its protocols are diverse (such as ISO 14443A/B, ISO 15693), and it has strong compatibility. For example, NFC technology is based on this frequency band.
IC(high frequency)usage scenario:Identity verification and payment: such as the second generation Id cards, public transportation cards, mobile payment, etc; Access control and membership system: Supports fast reading and writing as well as encrypted verification, such as hotel room cards or enterprise one-card systems; Smart tags: Library management, product traceability, etc., combined with NFC function to achieve data interaction.
2.ID (low frequency) Frequency 125Khz
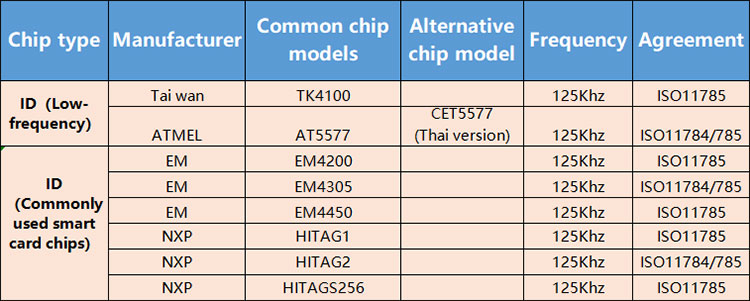
ID(low frequency)feature:Low-frequency chips transmit energy and data through inductive coupling and need to be close to the magnetic field range of the reader (usually < 10 centimeters). Its signal has good penetration through metals and liquids, but it has a small storage capacity (usually < 512 bits), slow read and write speed, and does not support simultaneous reading of multiple tags (without anti-collision mechanism).
ID(low frequency)usage scenario:Animal tracking: such as pet chips or livestock management, relying on their anti-interference capabilities; Simple access control systems: it is gradually being replaced by high-frequency ones, but still used in some low-cost scenarios.
3.UHF (Ultra High Frequency)
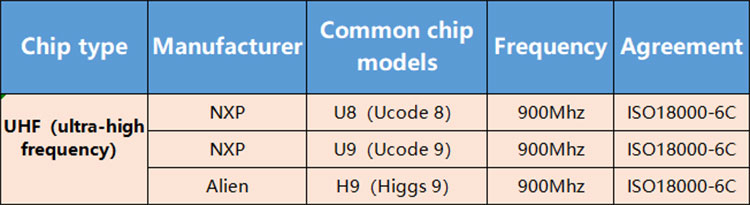
Ultra high frequency chip feature:The ultra-high frequency chip transmits through electromagnetic waves, with a reading distance of over 10 meters, supporting batch rapid reading (hundreds of tags per second). However, its signal is susceptible to interference from metals and liquids and requires special packaging (such as anti-metal tags).
Ultra high frequency chip usage scenario:Logistics and supply chain: Batch inventory of pallets and turnover boxes relies on long-distance group reading capabilities; Asset management: For instance, anti-metal labels are used for metal equipment and flexible labels for non-metal assets to support rapid inventory taking; Retail and warehousing: Clothing tags, inventory management, and batch data writing in combination with RFID printers.
Empower intelligent scenarios and create a safe, efficient and low-cost card making ecology.


